The teaching strategies and approach to this curriculum unit topic are varied, forward thinking, and promote brainstorming sessions as a means of student engagement. Additionally, multiple teaching strategies used in this curriculum unit encourage students to think independently and work collaboratively. As discovered along the way, reading a variety of teaching journal articles that discussed differentiation, as well as fellowship assigned journal articles, both served as a platform to convey clear integrated instruction.
The curriculum unit framework includes a series of steps, including a complete understanding of the American Disabilities Act, an Everfi-Endeavor STEM careers exploration course that offers a tailored approach to introduce topics relating to Science, Technology, Engineering, Math and Medical Careers, and ending with a Youth Health Service Corps service learning project.
As the first step in the framework, the students build a basis of knowledge regarding disabilities by defining and deconstructing the American Disability Act. Following their preliminary introduction to the ADA, the student will watch a 20 minute video, (https://www.adahospitality.org/at-your-service), produced by the ADA National Network Initiative and Hospitality that personalizes the difficulties met by those individuals touched by a disability. The video demonstrates how an individual is affected by their disability, how the public can help, and provides insight to students who have never seen or experienced someone who is disabled. The personalized narrative of the video provides students with an in depth view of individuals who are deaf, handicapped (wheelchair-bound), blind with a service animal, achondroplasia (dwarfism), and cerebral palsy. In addition, the introduction of medical terminology orients the student to conditions and diseases like achondroplasia, paraplegia, quadriplegia, and multiple sclerosis. Upon completed viewing of the video, the student will be `able to clearly understand the American Disability Act, its purpose and how it helps those afflicted by a disability.
Anatomy and Physiology courses discuss the Cardiovascular and Circulatory systems at great lengths. I had learned about the underlying diseases associated with both systems and procedures that would help alleviate or offer solutions to a patient with cardiovascular disease. Bypass surgeries and how the surgical procedure is performed were often discussed at great lengths. One day, while visiting the Yale Cadaver lab, I observed a medical student working on the thoracic region of his cadaver. I noticed what looked like a triple bypass on the humans coronary arteries but wasn’t sure because I had learned about it via textbooks and photos but never seen it live. I asked the medical student if it was a triple bypass and confirmed that indeed it was. This example is one of many personal experiences that I elaborate on and apply in the classroom. Had I not known about the text version of the bypass there would be a great chance had I seen it live I would have never noticed.
Once students have a solid understanding of the American Disability Act and individuals afflicted by a disability the next step is to apply the foundational knowledge to exploring STEM careers.
The second step of the unified teaching framework is the introduction of students to careers in STEM. The student will complete a STEM careers exploration software program called Everfi Endeavor STEM careers exploration module. The Everfi-Endeavor STEM careers exploration course is an interactive and individually tailored approach where students utilize a non-threatening platform to introduce topics relating to science, technology, engineering, math and medicine.
The Everfi, Endeavor unit encourages the student to reflect on STEM and how their propensities could connect them to future occupations in STEM fields. The student is empowered to make goal oriented decisions about their future in post-secondary education through soft skill development. Students gained contact experience to a variety of occupations and sectors of STEM career pathway by evaluating their own skills and interests. This teaching strategy aligns with the Connecticut Medical Careers, Career and Technical Education Standards, as well as the ASCA (American School Counselor Association) Nation and CASEL (Collaborative for Academic, Social, Emotional, Learning) competencies. The total curriculum consists of 6 lessons that approximately can take students 3-4 hours or more to complete. In summary, modules help prepare students for college and the workforce via various pathways and occupations utilizing interactive software driven by their personal interest.
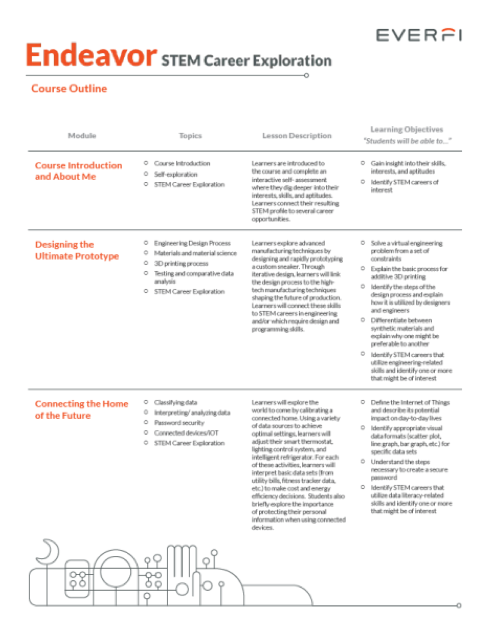
The Everfi interactive software program consists of six modules that make up this career exploration program, Course Introduction and About Me, Designing the Ultimate Prototype, Connecting the Home of the Future, Building the Perfect Playlist, Medical Machines, and My Field Guide.
The students begin with the Course Introduction and About Me Quiz. This module is introduced to the student via an interactive survey and questionnaire that compiles data about the students' learning style, problem solving skills, workstyle, and leadership skills. The module is pleasing to the eyes and colorful. As the student is engaged amidst a cartoon game like setting, they are self-exploring and self-assessing STEM career exploration. The culmination of the module includes the program matching STEM Careers tailored to the students interest based on the student’s answers during the self-assessment stage.
The program will then showcase a STEM occupation describing the STEM profession, required education or coursework needed, special projects this career may require, classes and skills that are necessary for the occupation and the average yearly salary one can expect. At the end of this module, the student will be able to search and explore potential careers using filters such as learning type, select years of education, and skills required. This module also provides an expected yearly salary based on the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
The remaining four modules can be completed by the student in any order they choose.
The Designing the Ultimate Prototypes module familiarizes the student with the engineering design process, special materials used, and the 3D printing process. For example, the student will be able to differentiate materials and explain why a certain material should be used for the design versus another due to its superiority. Upon completion of this module, the student will be able to identify an engineering STEM profession that may be of interest.
The Connecting the Home of the Future module acquaints the student with data and interpreting data. Students adjust smart thermostats, lights, and intelligent refrigerator, and then interpret data in the form of utility bills. Students are able to see the corresponding relationship between keeping the lights on and high electricity bills. This created a natural correction and most students went back into their virtual home and readjusted the light settings in order to lower the electrical bill.
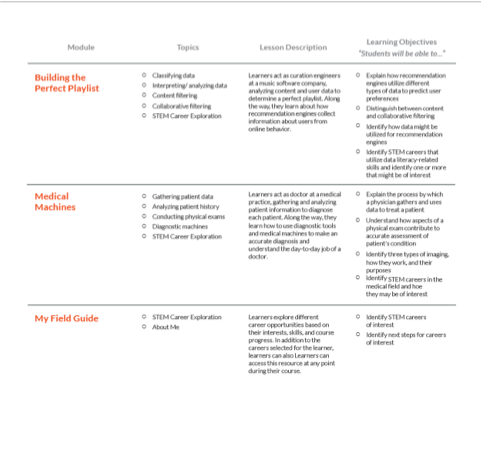
Most of the students found The Building of the Perfect Playlist module very difficult. It took students on average three attempts to complete this module. The module presented students with how recommendation engines collect information about user’s online behavior. Upon completion, students were able to distinguish between online content and collaborative filtering amongst other online users.
The Medical Machine module familiarizes the student with different medical machines and their uses in making a proper diagnosis. It also helped students understand the concept of what is it like to live a day in the life of a medical doctor. Upon completion, the student was able to identify three types of imagining, why they are used, and the primary purpose of why a doctor would prescribe such imagining.
My Field Guide is that last module the student completes for certification in STEM career exploration. This portion of the Everfi-Endeavor curriculum guides the student to identify the necessary steps for careers of interest.
Systematically the teaching strategies used thus far provide a scaffold type learning specific to this unit because of the diverse components associated with the curriculum unit topic. Allied health students who engage in this project have a solid understanding of health care, health care professions, and the contemporary issues in healthcare. Business students who participate in this project are enrolled in the course of Hospitality and Tourism. The collaboration with Ms. Kane and her students is a work in progress and to be reported at a later date. We are in the process of implementing the collaboration but have independently implemented in our classrooms for this school year. After we each compiled our teaching strategies we discovered that our coherent teaching plans were mirror image of each other even though they were fulfilled independently. It was a mutual understanding from the inception that in order to introduce this unit successfully, we had to use several teaching strategies and differentiation methods to assist and guide students.
At this point in the curriculum unit, students have the necessary framework, knowledge, and experiential learning that can be applied to service learning projects.
The following teaching plan incorporates the Youth Health Service Corps. The Youth Health Service Corps is a program that can help inspire a student to become a healthcare professional through meaningful service learning projects. The Youth Health Service Corps is a program conducted by AmeriCorps members. An AmeriCorps intern is assigned to a classroom and is available to assist the instructor to deliver meaningful assignments that relate to underserved communities.
Youth Health Service Corps is an organization that is grounded in four sets of educational standards. Academic framework, national health care skills standards, service learning standards, and developmental assets and the program consists of mainly two parts: training and service.
There are several parts of the YHSC student training module. The training module primarily consists of leadership qualities, service learning, vulnerable populations, ethics and legal issues, health careers exploration, and health care skills. The service module is consistent of a service learning project topic after students choose a particular disability to focus on. This pathway organically raises awareness for the student. Student will need to keep the chosen disability focus as it relates to the curriculum unit the topic.
Students begin working independently, then together in collaborative teams or pairs, and ultimately facilitate a way to address the American Disabilities Act, tourism and hospitality with applied biotechnological design.
The service learning projects aims to utilize the think-pair-share teaching strategy. Part one of the service learning project, focuses primarily on the students ability to think independently first. It is necessary for the student to reflect upon the past nine months of the Health Career Pathways I curriculum and the information that was learned throughout the year in order to complete a self-assessment on the American Disabilities Act, tourism and hospitality with applied biotechnological design.
In summary, part one of the service learning project is to motivate the student to recall everything they know or may know about the topic without access to anything other than the textbook used for over the course of the year. Upon successful completion, student submits their recall information for discussion with instructor. Once part one of the service learning project is approved, the student is given feedback, and is cleared to move on to part two of the service learning project.
Part two of the service learning project employs a variety of teaching strategies including inquiry based instruction and POGIL - process oriented guided inquiry learning. Both are student centered but differ in their research and data collection approach. Although inquiry based instruction is a student centered approach where the instructor is the facilitator, the POGIL method differs greatly and uses a small team approach or pairs, with the instructor as a facilitator. The instructor’s role is not a source or information but rather a source of initiation or expansion of the student’s idea or ideas. Students organically learn to discover information to support their research both individually and collaboratively as team members. As future health care professionals this type of mindset helps set the stage for their interactions later on a professional level when they assume the role as a health care professional attempting to problem solve for the best care possible for a patient. What makes the POGIL method so successful is that it has three major components:
- Teams are self-managed and utilize the instructor as a facilitator of learning not a source of information.
- The instructor guides students through exploration to discover greater understanding of topic.
- The instructor uses foundational knowledge of content to assist in higher-level thinking therefore applying the learned knowledge to newly discovered material.
Part two of the service learning project will address the need for services or medical devices guided towards students chosen target disability while keeping the curriculum topic name in the forefront. The focus is acquired knowledge based on the students research utilizing technology and reliable websites. The student will be able to answer the following questions based on their research:
- Basic definition of your disability
- Causes (causative and casual)
- Signs and symptoms
- Prevention
- Myths
- Management
- Local resources if any
- Vulnerable population
- Health disparities
- 10 questions or statistics on target disability
The following definitions are used as framework for the student:
Causative agents – pathogen or virus that directly causes a diseaseCausal factors – factors that increase the likelihood that a disease will developVulnerable populations – people that are more vulnerable to disease than othersHealth disparities – differences in the level of health people have due to unfair factors outside their control
Part three, the final portion of the service learning project is a reflective summary and oral presentation to fellow students. Students, in theory, summarize their journey through each step processing a self-reflection of the specified chosen disability and the implications it has on those individuals impacted by the said disability. What exactly it feels like to have the disability and what they can do or create to help them. The results are incredibly impressive!
Classroom Activities Teaching Methods and Resources
The following classroom activities, teaching methods, and resources utilized to deliver this curriculum unit.
American Disabilities Act National Network Initiative Video
https://www.adahospitality.org/at-your-service
Everfi Endeavor Stem Careers Exploration Course Outline
https://documentcloud.adobe.com/link/track?uri=urn%3Aaaid%3Ascds%3AUS%3A566f1052-8427-407d-912f-1a68e9e54391
Table 1.1
Academic standards that align with the New Haven Board of Education district standards
Demonstrate the concepts of basic disease processes.
The student will learn how to conduct research of common diseases, emerging diseases, and disorders.
The student will learn the Health Care Delivery System by understanding the health care providers roll and how it fits in a overall health care environment.
The student will be able to distinguish the range of services offered to patients in various health care facilities.
The student will understand how various state and federal agencies, regulatory boards, and insurance companies affect the delivery of healthcare.
The student will be exposed to ethical and cultural practices with to cultural, social, and ethnic differences within the healthcare environment.
The student will be able to interpret a Code of Ethics and the Patient's Bill of Rights.
Utilize procedures for reporting activities and behaviors that affect the health, safety, and welfare of others.