Electromagnetic waves are able to travel through empty space and do not require a medium. They are made up of oscillating electric and magnetic fields.6 These fields are travelling perpendicular to one another.
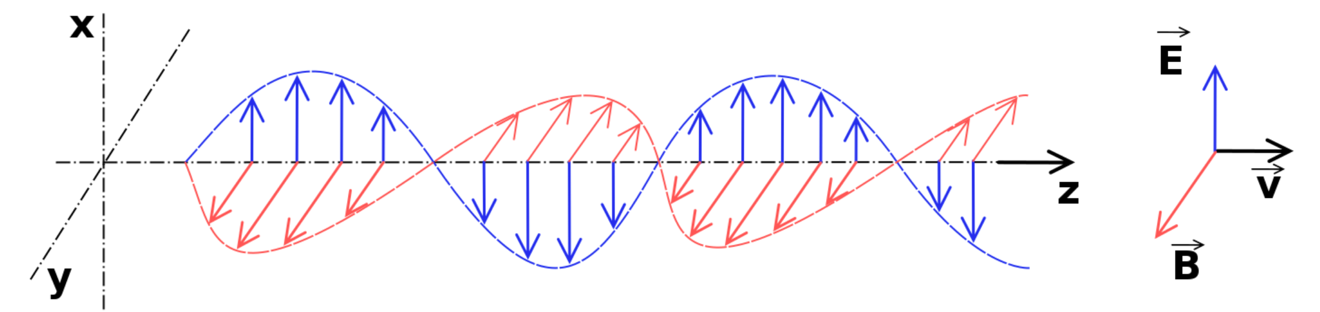
Figure 2: Electromagnetic waves are made of oscillating electric and magnetic fields at right angles to one another (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Onde_electromagnetique.svg).
The energy of EM waves is determined by the wavelength and frequency of these transverse waves. A wavelength is the distance between two identical points on a wave, e.g., two neighboring crests or troughs. Frequency is the number of complete waves passing a given point in a given amount of time measured in hertz (Hz).
Regions of the electromagnetic spectrum from lowest energy, lowest frequency and longest wavelength to highest energy, highest frequency and shortest wavelength are radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet light, x-rays and gamma rays. Each region has its applications.
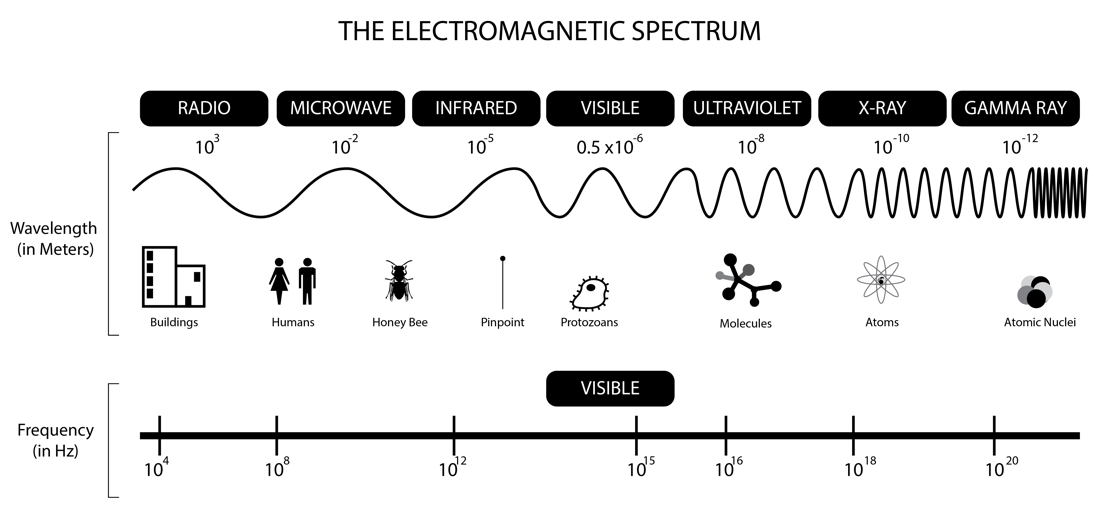
Figure 3: The electromagnetic (EM) spectrum with the seven regions in the order from the longest wavelength to the shortest wavelength with examples of applications. Also included are the frequency ranges for each region of the spectrum.7
|
Name of Region
|
Range of Frequency
(20)
|
Applications
|
Length Scale
|
|
Radio waves8
|
< 3 xHz
|
Radios, television and radar signals.
|
From about the length of a football to larger than the statue of liberty
|
|
Microwaves9
|
3x - 3xHz
|
Microwave ovens to cook food
|
A baseball
|
|
Infrared10
|
3x - 4xHz
|
TV remote
|
Diameter of a human hair.
|
|
Visible Light11
|
4x- 7.5xHz
|
Only range we can see
|
Thickness of a soap bubble membrane
|
|
Ultraviolet12
|
7.5x- 3x
|
Causing a sunburn and killing bacteria
|
Diameter of the rhinovirus.
|
|
X-Rays13
|
3x - 3xHz
|
Making images of bones
|
Diameter of an atom
|
|
Gamma Rays14
|
>3xHz
|
Released during nuclear reactions
|
Nucleus of an atom
|