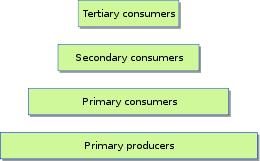
A food chain and food web are two expressions of the way in which energy is transferred from one organism to the next The food chain is a linear path that can be used to follow one particular creature and the food web is a visual illustration that explains the integral relationships between the many food chains in an ecosystem. However, both the food web and a food chain begin with the energy provided by the sun because it is this energy that is transferred and sustains all life on our planet. The next trophic level is a common link in both web and chain and then more diversion occurs according to habitat and ecosystem.
Beginning with the energy from the sun collected in phytoplankton through photo synthesis, each step in a food chain is called a trophic level. Phytoplankton are green plants that manufacture their own food through photosynthesis . These single celled microorganisms form the base of the food chain. Phytoplankton are called primary producers because they are able to produce their own energy, forming the pillar of the food chain. All food chains start with plants. Zooplankton occupy the second trophic layer because they eat phytoplankton. As a result, zooplankton are called primary consumers because they eat primary producers. Marine life that eats primary consumers occupy the third trophic level. Energy is lost as it is passed from one trophic level to the next. About 10% of energy is converted to body tissue from one trophic level to the next. Although energy is lost through the food chain as it is passed from prey to predator, material is not. Material from waste products and dead organisms are decomposed by bacteria and thus recycled back into the food chain as nutrients for phytoplankton.
59
Phytoplankton
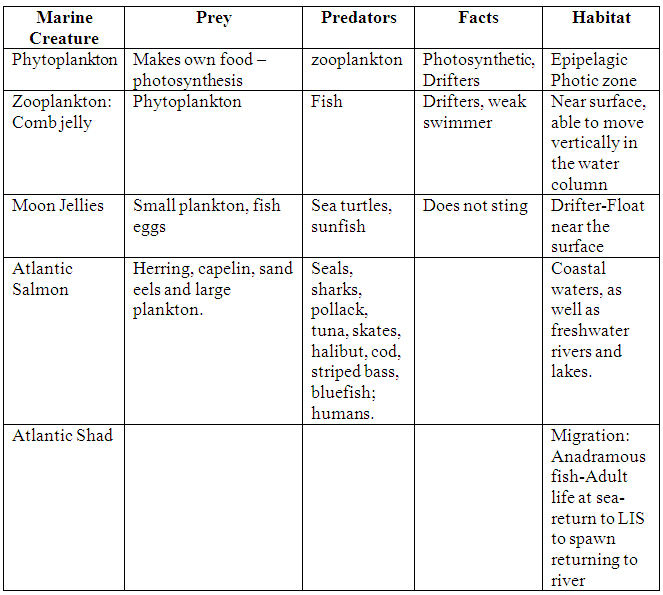
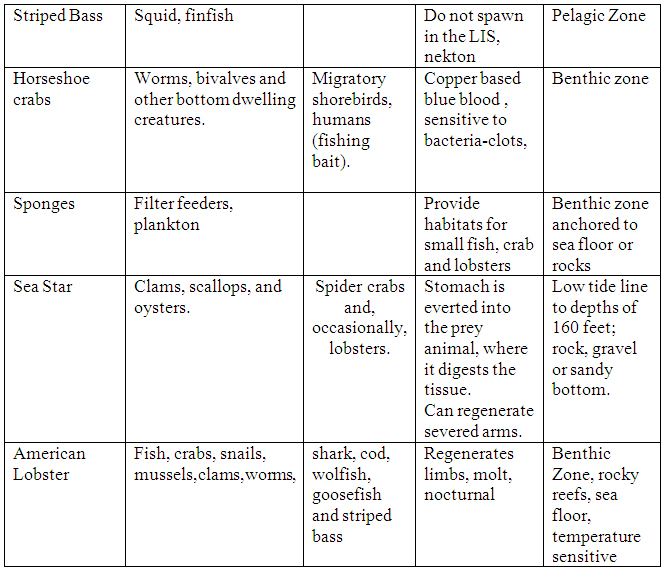
Creatures of the Long Island Sound
LIS Study