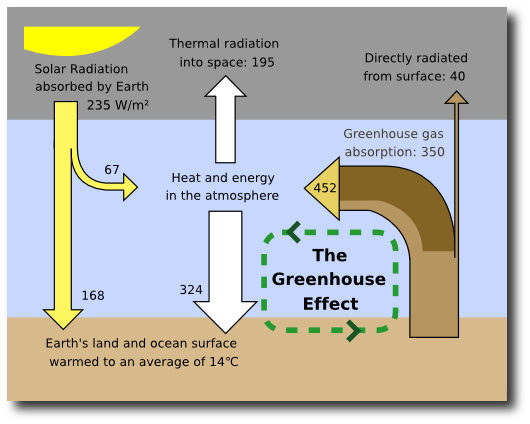
Our demand for energy affects the globe. Some of the recent changes in global climate such as higher temperatures and extreme weather frequency (tornadoes, hurricanes and blizzards,) are the result of an increased level of greenhouse gases in the environment. Greenhouse gases are produced when fossil fuels are burned. A fog of exhaust fumes and harmful gases produced by industrial processes often veil cities. The six main greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorcarbons and sulphur hexafluoride. Water vapor is also considered a greenhouse gas.
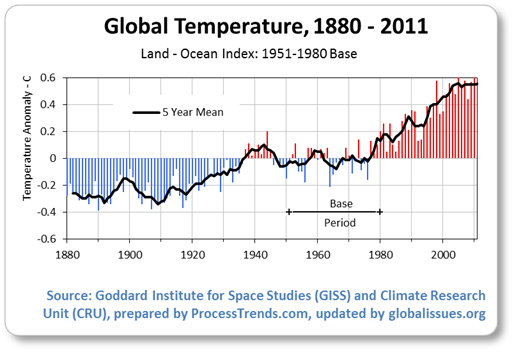
Many greenhouse gases are life-enabling, but, if the greenhouse effect becomes stronger, then more heat gets trapped than needed, and the Earth may become less habitable for humans, plants and animals. Carbon dioxide, though not the most potent,is the most significant one. Human activity has caused an imbalance in the natural cycle of the greenhouse effect. NASA's Earth Observatory is quoted below on the effect human activity is having on the natural carbon cycle. (Shah, Anup. Climate Change and Global Warming. http://www.globalissues.org/article/233.) In addition to the natural fluxes of carbon through the Earth system, anthropogenic (human) activities, particularly fossil fuel burning and deforestation, are also releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. When we mine coal and extract oil from the Earth's crust, and then burn these fossil fuels for transportation, heating, cooking, electricity, and manufacturing, we are effectively moving carbon more rapidly into the atmosphere than it is being removed naturally through the sedimentation of carbon, ultimately causing atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations to increase. Also, by clearing forests to support agriculture, we are transferring carbon from living biomass into the atmosphere (dry wood is about 50 percent carbon).The result is that humans are adding ever-increasing amounts of extra carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Because of this, atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations are higher today than they have been over the last half-million years or longer. Confusion about the difference between climate change and weather patterns arise when weather patterns and climate changes are mixed. "Weather patterns describe short term events, while climate change is a longer process that affects the weather. A warming planet is actually consistent with increasing cold, increasing rain and other extremes. The following charts explain the Greenhouse Effect and the trends in the rising of global temperature (Shah, Anup. Climate Change and Global Warming. http://www.globalissues.org/article/233.)