Global warming3 has been causing global temperatures to rise at higher levels and also causing severe climate changes across the planet. According to an article published in Scientific American4, if unchecked, global warming could increase the average temperature of the United States by 10ºF (Fahrenheit) over the next century. Global warming is caused due to the emission of greenhouse gases. These greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere resulting in the warming of the planet. This process is called the greenhouse effect. The gases responsible for causing this greenhouse effect are CO2, water vapor, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFC)5.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)6, greenhouse emissions caused by human activities also referred to as non-anthropogenic) such as the burning of fossil fuels have been steadily increasing in the United States and across the world. Similarly, the majority of the world’s emissions result from the generation of electricity, transportation, and other forms of energy production and usage. Carbon dioxide is emitted primarily through the burning of fossil fuels (oil, natural gas, and coal) and deforestation. According to the Global Carbon Project7, the top five countries that produce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from burning fossil fuels are China, U.S.A, India, Russian Federation, and Japan. Other sources that also contribute to global warming are Nitrous dioxide (N₂O) released through fertilizer usage, methane emitted through the raising of the cattle, harvesting of fossil fuels. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are a group of gases that do not occur naturally, are produced during commercials, industrial, and household uses, and are known for their ozone-depleting properties. In summary, the combustion of fossil fuels contributes to emissions of CO2, methane, and nitrous dioxide gases.
The Keeling Curve8 depicts the concentrations of CO2 at Mauna Loa Observatory located in Hawaii. In 1958, Charles David Keeling of Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UC San Diego, worked with scientists to create a method to record carbon dioxide (CO2) in our atmosphere. The measurements of CO2 in the atmosphere are due to the impact of human activities on the planet. According to scientists, there is a direct correlation between the burning of fossil fuels, rising CO2 levels, and the warming of the planet. The figure-1 shows the CO2 concentration (ppm) recorded on May 18, 2021. One can see a steady increase in CO2 levels from 1960 to date. This increase in the levels of CO2 is alarming to the scientific community. A quarter of the CO2 thus emitted into the atmosphere is being absorbed by the oceans, rivers, and lakes. This unit will focus on the impact of CO2 on ocean waters.
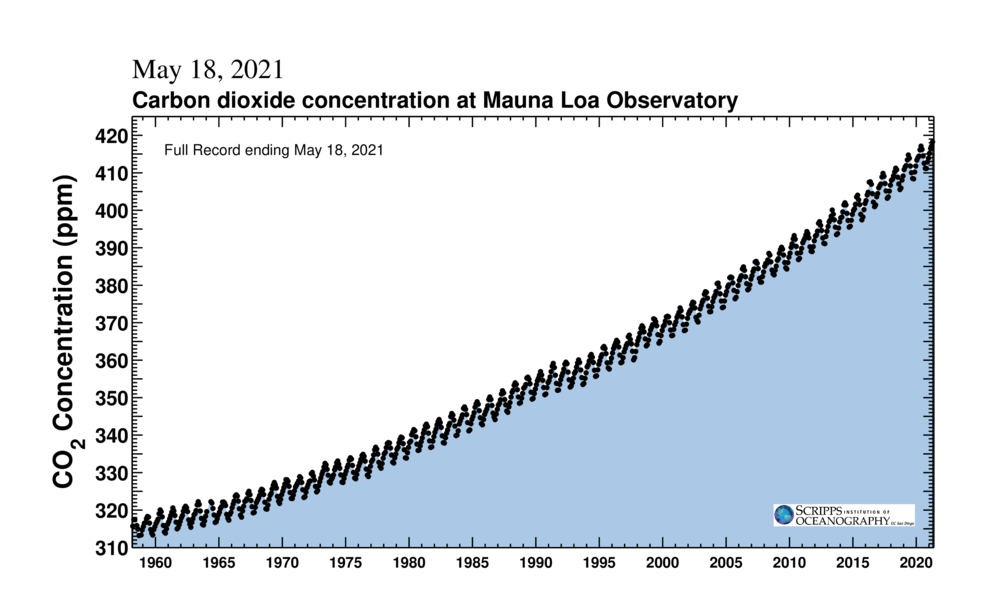
Figure-1: The Keeling Curve depicts the measurement of CO2 at Mauna Loa Observatory.